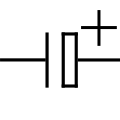Common circuit diagram symbols (US symbols)
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices (such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors) in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols can (because of remaining traditions) vary from country to country, but are today to a large extent internationally standardized. Some symbols represent components (such as vacuum tubes) which ceased to be used routinely as newer technologies were introduced.
- 1Standards for symbols
- 2Gallery of common electronic symbols
- 2.1Traces
- 2.2Circuit Return
- 2.3Sources
- 2.4Resistors
- 2.5Capacitors
- 2.6Inductors
- 2.7Transistors
- 2.7.1Unipolar
- 2.7.2Bipolar
- 2.8Diodes
- 2.9Antennas
- 2.10Vacuum tubes
- 2.11Switches
- 2.12Relays
- 2.13Lamps
- 2.14Current Limiters
- 2.15Transformers
- 2.16Acoustic Devices
- 2.17Miscellaneous
- 3Gallery of historical electronic symbols
- 3.1Capacitors (historical)
- 4References
There are several national and international standards for graphical symbols in circuit diagrams, in particular:
- IEC 60617 (also known as British Standard BS 3939).
- ANSI Y32.2-1975 (also known as IEEE Std 315-1975 or CSA Z99-1975)
- IEEE Std 91/91a: graphic symbols for logic functions (used in digital electronics). It is referenced in ANSI Y32.2/IEEE Std 315.
- Australian Standard AS 1102.
Different symbols may be used depending on the discipline using the drawing. For example, lighting and power symbols used as part of architectural drawings may be different from symbols for devices used in electronics. National and local variations to international standards also exist.
Symbols shown are typical examples, not a complete list.
2.1 Traces
-


IEC-style trace junction Trace crossing
2.2 Circuit Return
-



-
IEC-style ground (GND) symbol
-
Signal/Low noise ground (GND) symbol
-
IEC-style chassis-ground symbol
-
Sources
-
 Single cell, multi-cell battery
Single cell, multi-cell battery -
 Battery, multi-cell
Battery, multi-cell -
 Voltage source
Voltage source -
 Controlled voltage source
Controlled voltage source -
 Current source
Current source -
 Controlled current source
Controlled current source -
 AC voltage source
AC voltage source
Resistors[edit]
-
 (a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are American style symbols)
(a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are American style symbols) -
 (a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c)potentiometer (All of them are IEC style symbols)
(a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c)potentiometer (All of them are IEC style symbols) -
 Thermistor
Thermistor
Capacitors[edit]
-
 IEC-style capacitor, general symbol
IEC-style capacitor, general symbol -
 Capacitor, polarized (American)
Capacitor, polarized (American) -
 Capacitor, variable
Capacitor, variable -
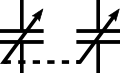 IEC-style ganged (co-moving) variable capacitors
IEC-style ganged (co-moving) variable capacitors -
 Trimmer capacitor
Trimmer capacitor
Inductors[edit]
-
 IEC-style air-cored Inductor
IEC-style air-cored Inductor -
 Inductor with magnetic core (IEEE Std 315)
Inductor with magnetic core (IEEE Std 315) -
 IEC-style tapped Inductor
IEC-style tapped Inductor
Transistors[edit]
Unipolar[edit]
-
 N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET) -
 P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET) -
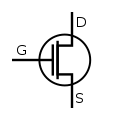 Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor -
 Enhancement mode, N-channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, N-channel MOSFET -
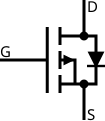 Enhancement mode, P-channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, P-channel MOSFET
Bipolar[edit]
-
 NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) -
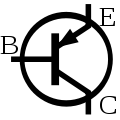 PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) -
 NPN darlington
NPN darlington -
 PNP darlington
PNP darlington
Diodes[edit]
-
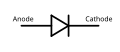 Diode
Diode -
 Zener diode
Zener diode -
 Tunnel diode
Tunnel diode -
 Schottky diode
Schottky diode -
 Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Light Emitting Diode (LED) -
 Photodiode
Photodiode -
 Varicap
Varicap -
 Shockley diode
Shockley diode -
 Silicon-controlled rectifier(SCR)
Silicon-controlled rectifier(SCR) -
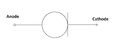 Constant-current diode
Constant-current diode
Antennas[edit]
-
 IEC-style antenna
IEC-style antenna -
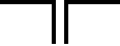 IEC-style dipole antenna
IEC-style dipole antenna -
 IEC-style loop antenna
IEC-style loop antenna -
 Loop antenna (IEEE Std 315)
Loop antenna (IEEE Std 315)
Vacuum tubes[edit]
-
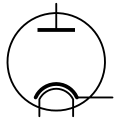 Vacuum tube diode
Vacuum tube diode -
 Vacuum tube triode
Vacuum tube triode -
 Vacuum tube tetrode
Vacuum tube tetrode -
 Vacuum tube pentode
Vacuum tube pentode
Switches[edit]
-
 Switch, Single Pole/Single Throw (SPST)
Switch, Single Pole/Single Throw (SPST) -
 Switch, Single Pole/Double Throw (SPDT)
Switch, Single Pole/Double Throw (SPDT) -
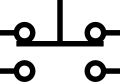
 Switch, Double Pole/Double Throw (DPDT)
Switch, Double Pole/Double Throw (DPDT) -
 Momentary switch, make (IEEE Std 315)
Momentary switch, make (IEEE Std 315) -
 Momentary switch, break (IEEE Std 315)
Momentary switch, break (IEEE Std 315) -
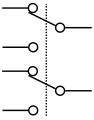
 Momentary switch, two circuit (IEEE Std 315)
Momentary switch, two circuit (IEEE Std 315)
Relays[edit]
-
 American-style relays, SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT
American-style relays, SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT -
 IEC relay symbol, SPDT
IEC relay symbol, SPDT
Lamps[edit]
-
 Indicating lamp (IEEE Std 315-1975)
Indicating lamp (IEEE Std 315-1975) -
 Incandescent lamp
Incandescent lamp -
 Incandescent light bulb(as an indicator)
Incandescent light bulb(as an indicator) -
 Neon lamp
Neon lamp -
 Light bulb
Light bulb
Current Limiters[edit]
-
 IEC Fuse (a), equivalent symbols (b,c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
IEC Fuse (a), equivalent symbols (b,c) (IEEE Std 315-1975) -
 Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) -
 Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Transformers[edit]
-
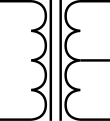 Transformer with center tap
Transformer with center tap -
 Transformer with two secondary windings
Transformer with two secondary windings -
 Current Transformer
Current Transformer -
 Zero-Sequence Current Transformer (ZSCT) (a.k.a. window-type current transformer)
Zero-Sequence Current Transformer (ZSCT) (a.k.a. window-type current transformer) -
 Bushing-Type Current Transformer
Bushing-Type Current Transformer -
 Voltage Transformer
Voltage Transformer
Acoustic Devices[edit]
-
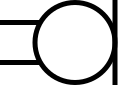 IEC-style microphone
IEC-style microphone -
 Microphone (IEEE Std 315)
Microphone (IEEE Std 315) -
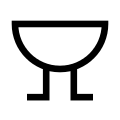 Buzzer
Buzzer -
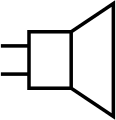 Loudspeaker (IEEE Std 315)
Loudspeaker (IEEE Std 315)
Miscellaneous[edit]
-
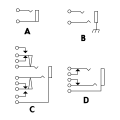 Phone jacks
Phone jacks -
 Operational amplifier
Operational amplifier -
 Ferrite bead ring (IEEE Std 315)
Ferrite bead ring (IEEE Std 315)
Gallery of historical electronic symbols[edit]
The shape of electronic symbols have changed over time. Some symbols were more prevalent in some countries. The following are historic electronic symbols that might be found in old electronic books and schematics.
Capacitors (historical)[edit]
References
- Circuit Symbols for all Electronic Components. Talking Electronics, 2013. Retrieved 01 Apr 2015.
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic Symbols. RapidTables, 2012. Retrieved 17 April 2016.